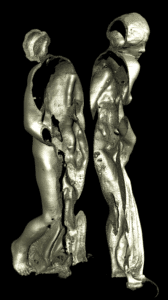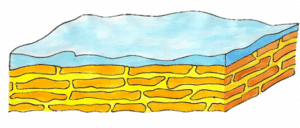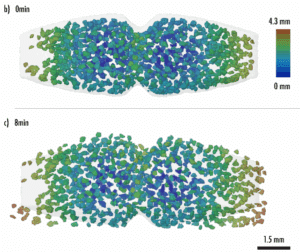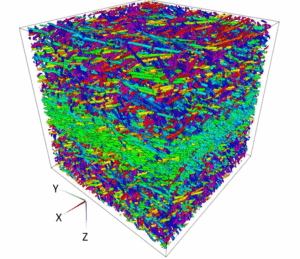
Why choose X-ray tomography or microCT?
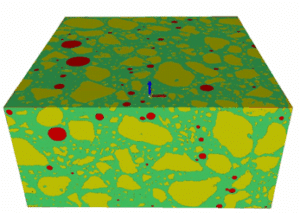
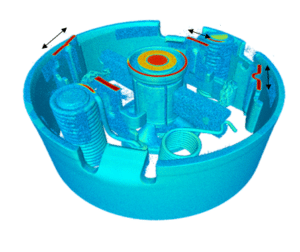
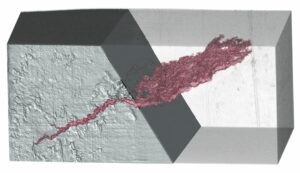
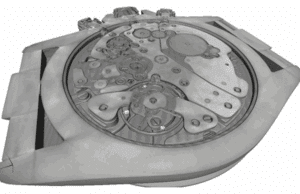
X-ray tomography is now a reference method for non-destructive three-dimensional imaging. Its principle is based on capturing a large number of X-ray images from different angles, which are then combined digitally to reconstruct the internal structure of an object. Tomography, which has become essential in various fields such as material