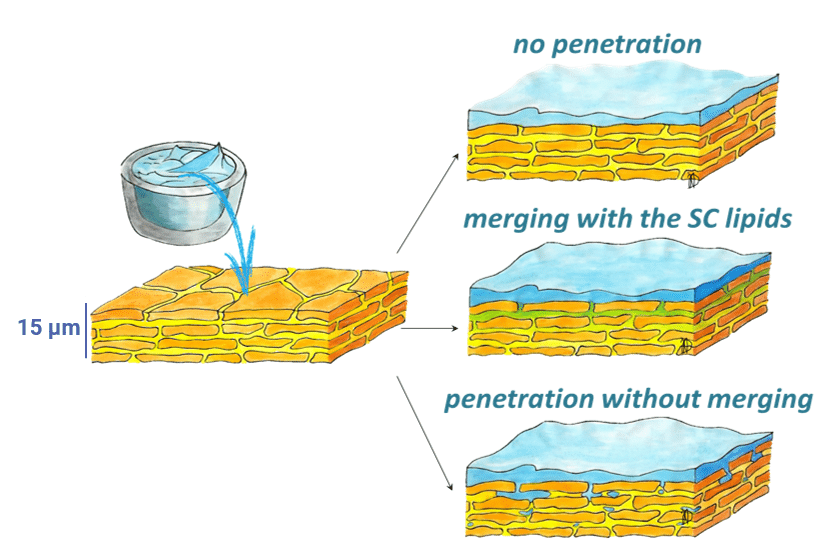
Unveiling the impact of topical formulations on the organization of stratum corneum lipid barrier using X-ray micro-diffraction
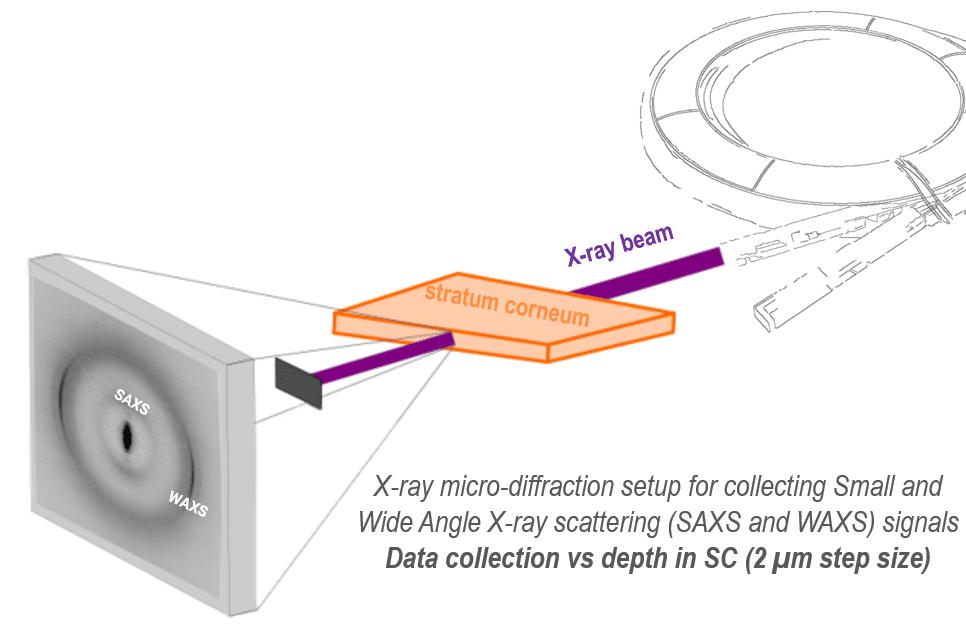
X-ray diffraction reveals the structural organisation of the intercorneocyte lipids in the stratum corneum X-ray microdiffraction (µXRD) unveils the structural…